Integrated Pest Management ?
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is more than a collection of strategies or a mere buzzword; it’s a systematic and sustainable approach to controlling pests. Rooted in science, IPM encompasses a combination of practices that aim to reduce the reliance on harmful chemicals. By leveraging biological, cultural, physical, and chemical methods in harmony, IPM minimizes risks to people, animals, and the environment. It involves continuous monitoring, precise identification of pests, and measured interventions that consider the broader ecosystem, thus promoting overall balance and health.
Importance and Relevance of IPM
In an era where the notion of sustainability has moved from being a trend to an essential part of our daily lives, IPM has gained tremendous significance. Its principles echo the global call for responsible stewardship of our planet. By emphasizing prevention over eradication and choosing environmentally friendly methods, IPM goes beyond mere pest control. It’s a philosophy that resonates with our growing awareness of environmental care and the need for harmonious coexistence with nature. This human-centric approach aligns with global efforts to combat climate change, protect biodiversity, and foster sustainable agriculture and urban living.
Brief Overview of Techniques
The techniques utilized in IPM are as varied as nature itself. From the simplest traps that capture pests without harming non-target organisms to sophisticated chemical solutions designed with the utmost precision, each method plays a specific role. Biological controls utilize natural predators or parasites, while cultural methods adjust environmental conditions to make them less hospitable to pests. Mechanical and physical controls range from manual removal to barriers and traps, and chemical controls are used judiciously, often as a last resort. Together, these techniques form a symphony of protection, each playing a part, yet working in concert to create an effective, sustainable solution. The rich variety ensures that IPM can be tailored to specific needs and environments, making it a versatile and adaptable approach to pest management.
The expanded introduction offers a deeper insight into the concept of Integrated Pest Management, underscoring its complexity, relevance, and diverse techniques that contribute to its effectiveness. By shedding light on these aspects, the introduction sets the stage for a detailed exploration of IPM in the subsequent sections.
Principles of IPM
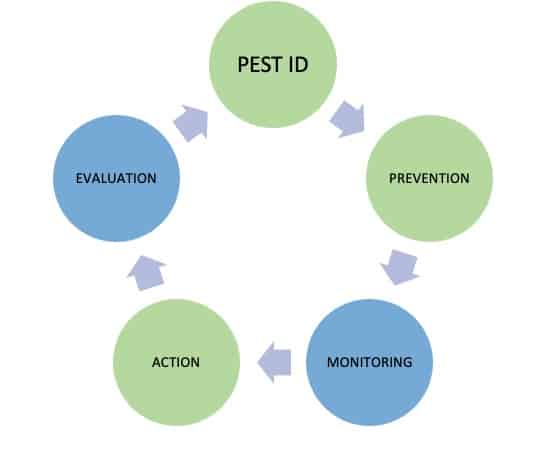
Monitoring and Identification
IPM doesn’t leap into action without thought; it starts with understanding, observing, and recognizing pests. Constant monitoring of the environment is essential to detect the early signs of infestation. Accurate identification of the pest ensures that the appropriate measures are taken, as different pests require specific strategies. This principle avoids unnecessary treatments, thus saving resources and further protecting non-target organisms.
- Prevention
As the saying goes, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure, and nowhere is this truer than in IPM. By focusing on preventing pest populations from reaching damaging levels, IPM minimizes the need for reactive interventions. This might include selecting disease-resistant plants, maintaining healthy soil, or creating barriers to entry. Prevention is the cornerstone of the IPM philosophy, integrating cultural, biological, and physical strategies to keep pests at bay without harmful chemicals. - Intervention
When preventive measures are not enough, intervention becomes necessary. Here, IPM employs a variety of targeted approaches:
- Biological Control: Nature’s way of maintaining balance. This method uses natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to manage pest populations.
- Chemical Control: Science’s answer, applied with precision and care. This may include synthetic or natural pesticides, but only when necessary, and in the least toxic formulations.
- Cultural Control: Creating harmony with the environment. Practices like crop rotation, sanitation, and habitat manipulation make the environment less inviting to pests.
- Mechanical and Physical Control: Sometimes, hands-on is the way. This can mean hand-picking pests, using traps, or creating physical barriers to protect plants and buildings.
- Evaluation
Evaluation isn’t a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process in IPM. The efficacy of treatments and interventions must be measured and assessed regularly. This reflective process ensures that strategies are working as intended and can be adjusted if needed. Evaluation promotes continuous learning and improvement, keeping IPM practices up-to-date with the latest research and technology.
Benefits of IPM
- Environmental Benefits
Integrated Pest Management is green in practice, not just in name. By prioritizing non-chemical methods and using chemicals sparingly and judiciously, IPM reduces pollution of water, soil, and air. The practice of monitoring and precise identification helps avoid harm to non-target organisms, such as beneficial insects or birds. The preservation of natural ecosystems, reduction in the carbon footprint, and the safeguarding of biodiversity are intrinsic to the IPM approach. It’s a method that respects the delicate balance of nature and strives to work within it rather than overpowering it. - Economic Advantages
IPM isn’t just about environmental consciousness; it also makes economic sense. By focusing on prevention and careful monitoring, it reduces the need for costly chemical interventions. The use of natural predators or cultural practices often costs less than synthetic chemicals. Furthermore, IPM can lead to better crop yields by keeping pests at bay without harming the plants or the soil they grow in. It’s an approach that saves green of another kind: money. Whether for large-scale agriculture or small home gardens, IPM can provide cost-effective solutions that make both environmental and financial sense. - Social and Health Benefits
The advantages of IPM extend into the social fabric of our communities. By reducing reliance on harmful chemicals, IPM helps create a healthier environment for people. It minimizes exposure to toxins for farmers, gardeners, and consumers alike. In urban settings, it helps maintain healthy public spaces free of both pests and hazardous chemicals. Moreover, IPM aligns with a growing societal emphasis on sustainable living and responsible consumption. It fosters education and community involvement, encouraging a collective approach to pest management. A community truly thrives when it’s free of harmful pests and chemicals, and IPM helps create such vibrant, healthy spaces.
The benefits of Integrated Pest Management go beyond mere pest control, offering a broad spectrum of advantages that touch various aspects of life. From the environmental stewardship that protects our planet to the economic savings that make sense to our wallets, and the social and health gains that enrich our communities, IPM stands as a holistic, responsible approach to dealing with pests. Its principles and practices resonate with a modern world seeking sustainable, thoughtful solutions to age-old challenges.
Methods and Techniques
- Pest Identification
Know thy enemy is a principle that is central to IPM. Accurate pest identification is crucial in determining the correct course of action. Misidentification can lead to unnecessary or ineffective treatments, wasting both time and resources. Pest identification includes understanding the pest’s lifecycle, behaviour, and the particular damage it may cause. Tools like traps, visual inspections, and sometimes even laboratory analyses might be used. The goal is to understand the specific pest’s nature and needs so that it can be managed effectively and with minimal harm to the surroundings. - Setting Action Thresholds
When to act is not a decision made on a whim; it’s a science and an art in IPM. Action thresholds are specific levels at which pest populations or environmental conditions indicate that pest control action must be taken. These thresholds are set based on research, field experience, and an understanding of the particular ecosystem. They help in making informed decisions about when intervention is necessary and what kind of intervention is appropriate. This principle ensures that actions are taken only when needed, minimizing unnecessary interventions. - Preventive Measures
Prevention in IPM is not just about immediate actions; it’s about building barriers, both real and figurative, against potential infestations. This includes proper sanitation, selecting resistant varieties of plants, maintaining optimal soil health, and installing physical barriers like screens or nets. By creating an environment where pests are less likely to thrive, these measures help in avoiding problems before they start. It’s a proactive approach that minimizes the need for reactive control methods later. - Control Methods
When prevention and thresholds indicate the need for intervention, IPM provides a toolkit of control methods:
- Biological: Let nature fight the battle. Utilizing natural predators, parasites, or disease organisms to control pests can be an effective and environmentally friendly solution.
- Chemical: When needed, but only then, and precisely. Chemical control methods include the use of pesticides, but in the most targeted and minimal way, often as a last resort.
- Cultural: Harmony with the surroundings. This involves practices like crop rotation, intercropping, or proper irrigation techniques that make the environment less conducive to pests.
- Mechanical: Sometimes, the right tool for the job is a mechanical one. Traps, barriers, or even handpicking can be effective ways to manage pests without chemicals.
The methods and techniques of IPM represent a harmonized blend of science, experience, and respect for nature. Through a combination of understanding, precision, prevention, and diverse control methods, IPM provides a comprehensive approach to pest management. Its flexibility and adaptability allow it to be applied across various contexts, from agriculture to urban settings, always with an eye towards minimal harm and maximum effectiveness. It’s a reflection of a thoughtful approach to a complex challenge, integrating the best of what both nature and human innovation have to offer.
Challenges and Barriers
- Implementation Issues
Implementing IPM is not always a straightforward process. It requires coordination, adaptation, and sometimes a shift in traditional practices. Constraints like resource availability, lack of trained personnel, or conflicting short-term goals can pose hurdles. Yet, these challenges can be overcome, and the benefits of IPM make it worth the effort. - Regulatory Constraints
Navigating the red tape of laws and regulations can be a challenge. Different regions may have varying rules governing pest control methods, pesticide use, or environmental protection. Compliance with these regulations is essential but can also constrain the flexibility of IPM practices. - Education and Awareness
Understanding IPM requires knowledge and awareness. Whether it’s farmers, gardeners, policymakers, or consumers, education is vital. A lack of understanding can lead to resistance, misuse, or underutilization of IPM techniques. Investing in education and building awareness is key to unleashing the full potential of IPM.
IPM is more than just pest control; it’s a philosophy that embodies respect for our planet and ourselves. It reflects a commitment to sustainable living, responsible consumption, and harmonious coexistence with nature.

On-Teime Service

5 START SERVICE BASED ON 100+ GOOGLE REVIEWS
PET & FAMILY FRIENDLY TREATMENT

ALL YEAR-ROUND PROTECTION
Take Back Control Now
8
REASON TO CHOOSE SAFE PEST CONTROL
- Guarantee protection all year-round
- 30 Years Collective Experience
- An impeccable reputation across Sydney's Suburbs
- Certified treatments & written Warranty On all work carried out
- Family Owned & Operated
- Rated #1 Pest Control In Sydney
- No Mess, No Smell
- Family & Pet Friendly Treatments

Book Your Free Cockroach Inspection Online
We Specialise In the following pest control Services
WE ARE HERE MON-SAT 8AM TO 5PM, CALL US NOW
Speak to a pest specialist. Call 1300 119 085 or Click Here
Spider Problem? Call to Book Your Free Inspection
Are eight-legged visitors turning your home into a haunted house? Call us to book a free inspection. We provide expert solutions for all spider-related problems, offering you a safe, spider-free environment.